MBST® focuses on the body’s natural healing power. Cells have a limited lifespan, and wear and tear, overloading, and injuries can damage the body’s tissues. In a healthy body, these damages often go unnoticed as old tissue is replaced by new cells. This is how injuries and wounds heal, with some tissues healing faster than others.
At times, the body cannot manage necessary repairs on its own or can only do so very slowly. When cell functions and metabolism are disrupted due to age-related wear and tear, injuries, or tissue damage, repair processes cannot be completed as needed. MBST® aims to trigger natural regeneration processes and promote healing.
Study data shows that MBST® affects various natural processes in the body. It can stimulate, trigger, or reduce certain biophysical processes that influence cell condition and help restore normal cell functions. Small physical changes at the molecular level can have a significant impact on the body. MBST® uses physical principles to influence the biological causes of conditions and injuries.
We are constantly involved in basic research and studies in collaboration with various universities to deepen our understanding of how MBST® works. Through this, we have confirmed several mechanisms that influence its regenerative, pain-relieving, and anti-inflammatory effects.*
I’m cycling again, going dancing with my wife, and can even go on longer hikes. For me, the attempt was worth it.
– Wolf H., 72 years old
I'm active again!
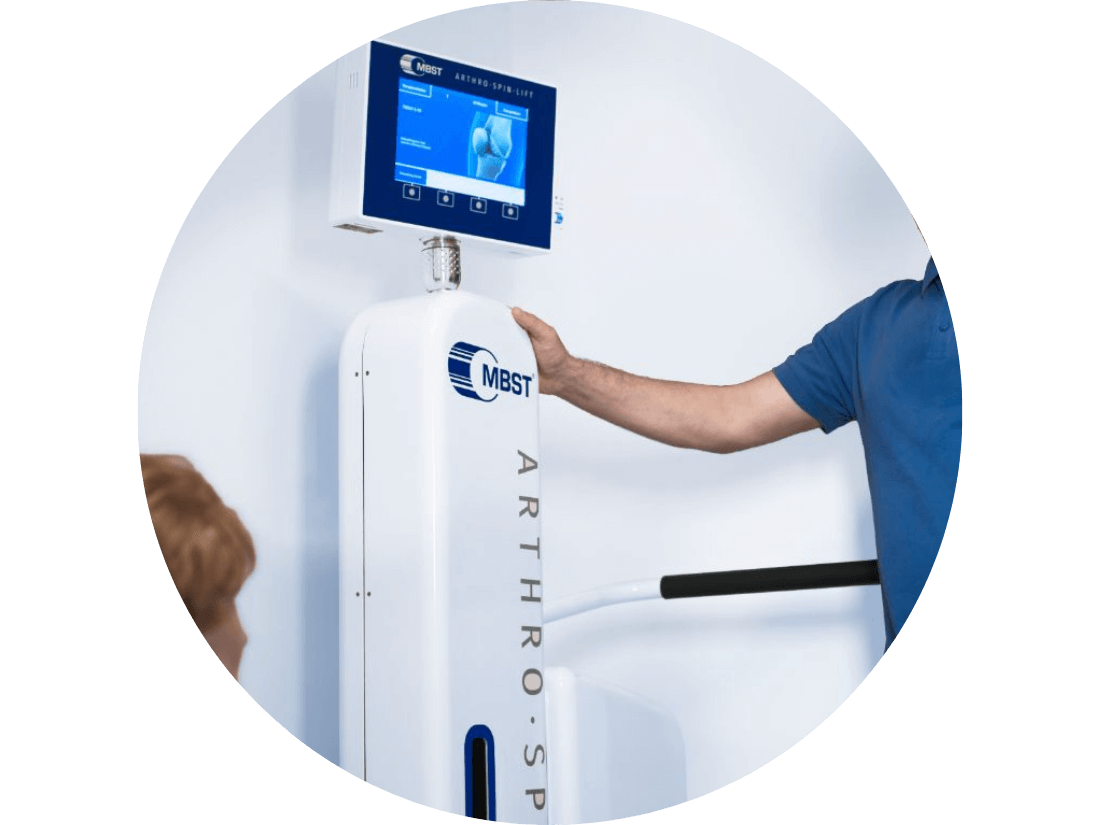
Post-OP Treatment
in use internationally
therapy hours without side effects or interactions
Everything is okay again.
Knee osteoarthritis
Steinecker-Frohnwieser et al. 2014, J. Orthop. Rheum., 9/2014 | Steinecker-Frohnwieser et al. 2018, Clin Exp Rheumatology 36, 294–301 | Thöni et al. 2021, Chronobiology International, DOI: 10.1080/07420528.2021.1910288 | Steinecker-Frohnwieser et al. 2021, Int J Molecular Sciences 22, 5959 | Mann et al. 2022, frontiers in cellular neuroscience 16, 859545 | Temiz-Artmann et al., 2005, Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 27(6), 391-394 | Rad et al. 2024, Cells 13, 1544, DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13181544 | Thöni et al. 2022, iScience 25, 105536
You are currently viewing a placeholder content from Google Maps. To access the actual content, click the button below. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More Information